Are electric cars really worth the investment? Advantages and disadvantages
Electric cars are rapidly changing the car market as an attractive alternative to conventional vehicles. The increasing focus on ecology and the desire to reduce dependence on fossil fuels is driving the choice of this innovative technology. Electric cars offer many advantages such as lower running costs, quiet running, etc. However, they also have disadvantages, including a limited network of charging stations and a higher initial cost. The question is therefore whether electric vehicles can change the transport sector and what trade-offs might be involved in choosing this modern means of transport.
Advantages of electric cars
- Lower emissions. One of the main advantages of electric cars is their reduced environmental impact. Most of the emissions (50-70 g CO2/km) come from the CO2 produced by the battery, which is distributed over the distance travelled by the electric car over its lifetime. The average diesel or petrol car emits 150-200 g CO2/km every time it is driven.

- More efficient operation. Energy efficiency in vehicles is measured by how much fuel energy is converted into actual power to move the vehicle. Electric cars far outperform fuel-powered cars in this respect, with an impressive 85-90% energy efficiency. Internal combustion engine vehicles convert only about 20% of the energy stored in petrol into power for movement
- Lower fuel consumption. Although charging costs vary from one European country to another, the cost of electricity per kilometre is lower than petrol or diesel. According to data for 2023, the average cost of electricity in Lithuania was around €0.20/kWh. The average electric car consumes around 15-20 kWh/100 km. So a 100 km range can be covered for 3-4 EUR. A conventional car consumes around 6-7 litres of fuel per 100 km. If 1 litre of fuel costs €1.7, a 100 km journey in a conventional car will cost €10-12.
- Less noise. Unlike fuel-powered vehicles, electric cars only make noise due to wind resistance and tire grip. In fact, to protect pedestrians, legislation requires electric cars to make at least 56 dB of noise when driving. Nevertheless, they are still much quieter than conventional vehicles, with noise levels of 70-90 dB. This is particularly important in large cities, where noise levels often exceed safe limits for health.

- Requires less maintenance. An electric car can be 20% to 50% cheaper to maintain than a conventional vehicle. EVs do not need regular engine oil changes, have far fewer moving parts and are less likely to break down. Replacing the battery of an electric car is more expensive, but most manufacturers offer warranties and minimal costs for the first 8-10 years.
- Government subsidies and incentives. In Lithuania, subsidies of up to €5,000 are available for EV buyers. In some countries, they benefit from reduced road tax rates, free parking or the right to drive in special lanes.
Disadvantages of electric cars
- High initial investment. It is still more expensive to buy an electric car than a fuel-powered car. In 2023, the average price of a new electric car in Europe was around €35,000 compared to around €25,000 for a petrol car.
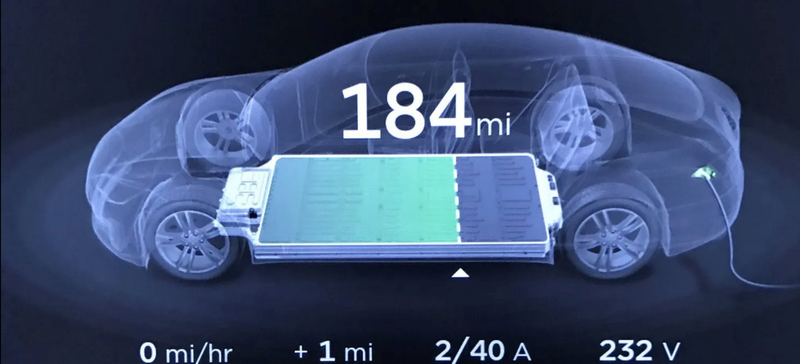
- Limited range. According to many surveys, distance anxiety is one of the most important criteria when choosing a vehicle. In 2023, the average battery capacity of an electric car was around 60 kWh, giving a range of around 350 km. A fuel-powered car with a full tank has an average range of around 700 km.
- Long charging times. It takes just a few minutes to fill the tank completely. Charging an electric car can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours - much longer than a typical coffee break (10-20 minutes). This can be inconvenient when travelling, especially when fast charging stations are not easily accessible.
- Lack of charging points. Although the number of charging points for electric vehicles is increasing rapidly, they are still limited, especially in rural areas and smaller towns. Currently, there are around 375,000 public EV charging points across Europe. In Lithuania, there are only 600 today. This can cause inconvenience when planning trips.

- High battery replacement costs. Depending on the EV model, the cost of replacing the battery ranges from €5,000 (e.g. Nissan Leaf 40 kWh) to €20,000 (e.g. Tesla Model S 75 100 kWh). The cost of a new battery for a normal car is between €50 and €150.














